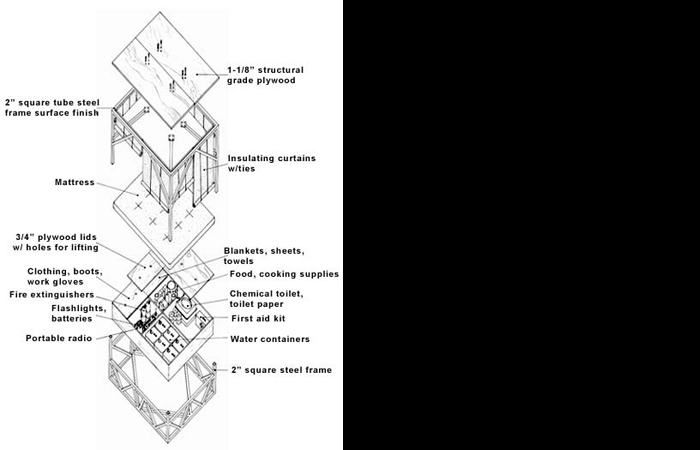
earthquake survival bed
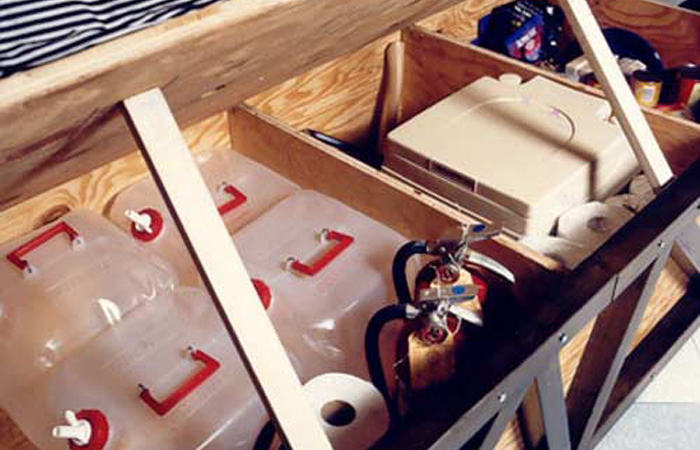
Designed following the San Francisco Loma Prieta earthquake in 1989, this bed was intended to prevent people from being trapped due to a temblor. Designed as a survival shelter where individuals could seek safe refuge until rescue workers appeared, this bed provides a space where two people can live for a week.
Framed with 2-inch tubular steel and 1 1/8-inch plywood, these two elements allow the bed to resist over 6,000 pounds of vertical roofload. The design possesses a roll cage similar to that of racing cars. The bed's base acts as a storage unit, including items for survival. The side curtains consist of insulated material which form an enclosure to minimize heat loss during occupancy in an emergency state. Both collapsible and mobile in form, the survival bed is not regulated as a permanent part of a living space.